This post was originally published on Eco Watch
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has issued the first-ever nationwide, legally enforceable limits on harmful per- polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) — known as “forever chemicals” — in drinking water.
The rule is the biggest leap so far in EPA’s PFAS Strategic Roadmap and will lower exposure to the toxic substances for roughly 100 million people, a press release from EPA said.
“Drinking water contaminated with PFAS has plagued communities across this country for too long,” said Michael S. Regan, EPA administrator, in the press release. “Our PFAS Strategic Roadmap marshals the full breadth of EPA’s authority and resources to protect people from these harmful forever chemicals. Today, I am proud to finalize this critical piece of our Roadmap, and in doing so, save thousands of lives and help ensure our children grow up healthier.”
PFAS exposure has been associated with cancer, heart and liver disease and damage to the development and immune systems of children and infants. The new rules will lead to tens of thousands of fewer related health issues while preventing thousands of fatalities.
EPA is making funding available to implement the new rule through the Biden-Harris administration’s Investing in America agenda. Through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, nearly $1 billion will be accessible to assist states and territories with carrying out testing for PFAS, public water system treatment and help for private well owners with addressing contamination from forever chemicals. A total of $9 billion is being invested to assist communities with PFAS and other contaminants in drinking water, as well as $12 billion for general improvements to drinking water.
Last year, a study by the U.S. Geological Survey found PFAS in almost half of tap water samples in the country.
“The first national drinking water standards for PFAS marks a significant step towards delivering on the Biden-Harris Administration’s commitment to advancing environmental justice, protecting communities, and securing clean water for people across the country,” said Brenda Mallory, White House Council on Environmental Quality chair, in the press release.
The new rule establishes limits for PFOA, PFNA, PFOS, PFHxS and HFPO-DA — known as “GenX Chemicals.”
“For PFOA and PFOS, EPA is setting a Maximum Contaminant Level Goal, a non-enforceable health-based goal, at zero. This reflects the latest science showing that there is no level of exposure to these contaminants without risk of health impacts, including certain cancers,” the press release said.
For each of PFOS and PFOA, the enforceable maximum levels will be four parts per trillion (ppt).
“This standard will reduce exposure from these PFAS in our drinking water to the lowest levels that are feasible for effective implementation,” according to the press release.
Maximum levels for PFHxS, PFNA and GenX Chemicals will be 10 ppt.
The EPA rule also limits mixtures of two or more of PFNA, PFBS, PFHxS and GenX chemicals.
“We learned about GenX and other PFAS in our tap water six years ago. I raised my children on this water and watched loved ones suffer from rare or recurrent cancers. No one should ever worry if their tap water will make them sick or give them cancer,” said Emily Donovan, Clean Cape Fear co-founder. “We will keep fighting until all exposures to PFAS end and the chemical companies responsible for business-related human rights abuses are held fully accountable.”
Approximately six to 10 percent of the public drinking water systems — 66,000 of them — subject to the new rule may need to take steps to reduce PFAS in order to meet the new standards. Public water systems will have three years to finish their initial monitoring for forever chemicals. Meanwhile, they will be required to inform the public of PFAS levels in their drinking water. When PFAS is detected at levels in excess of the standards, solutions must be implemented within five years.
“The new limits in this rule are achievable using a range of available technologies and approaches including granular activated carbon, reverse osmosis, and ion exchange systems,” the press release said. “For example, the Cape Fear Public Utility Authority, serving Wilmington, NC — one of the communities most heavily impacted by PFAS contamination — has effectively deployed a granular activated carbon system to remove PFAS regulated by this rule. Drinking water systems will have flexibility to determine the best solution for their community.”
EPA will host informational webinars available to the public in the coming weeks. Information is available on the PFAS drinking water regulation website.
“For decades, the American people have been exposed to the family of incredibly toxic ‘forever chemicals’ known as PFAS with no protection from their government. Those chemicals now contaminate virtually all Americans from birth. That’s because for generations, PFAS chemicals slid off of every federal environmental law like a fried egg off a Teflon pan,” said Ken Cook, president and co-founder of Environmental Working Group, in the press release. “There is much work yet to be done to end PFAS pollution.”
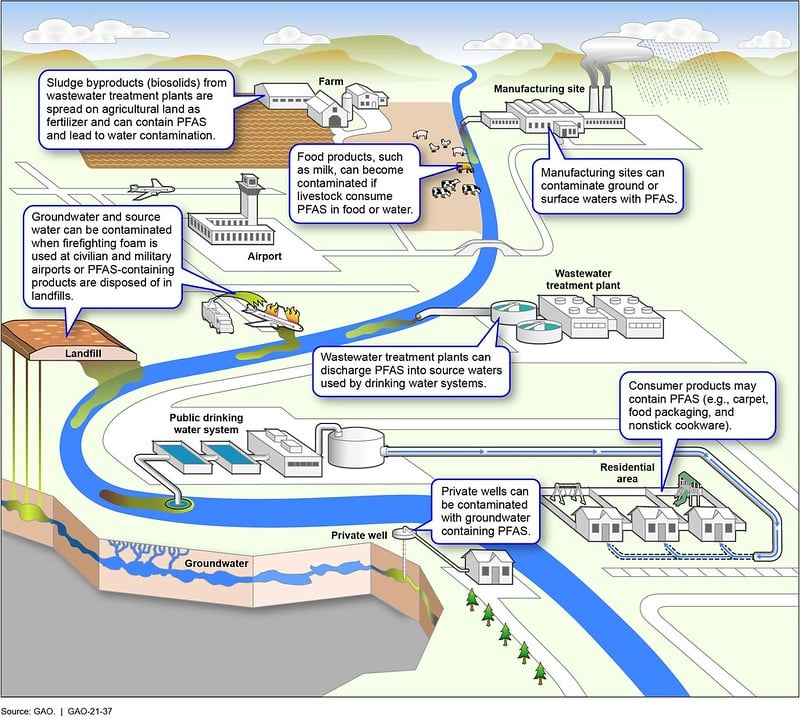
Examples of how PFAS enter the environment and water, from a U.S. GAO report published in 2021. U.S. Government Accountability Office
The post EPA Announces First-Ever Rule Limiting PFAS ‘Forever Chemicals’ in Drinking Water appeared first on EcoWatch.




0 Comments