This post was originally published on Eco Watch
As deadly wildfires continue to blaze around greater Los Angeles, the economic cost of the fires has now been estimated to be over $200 billion. That has made this tragedy, which started on January 7, potentially the most expensive wildfire event in U.S. history.
At least 24 people have died as of the time of writing, according to CBS News.
As Earth.org reported, the fires have already burned around 40,000 acres and counting, totaling an amount of land larger than San Francisco. More than 12,300 structures have been destroyed.
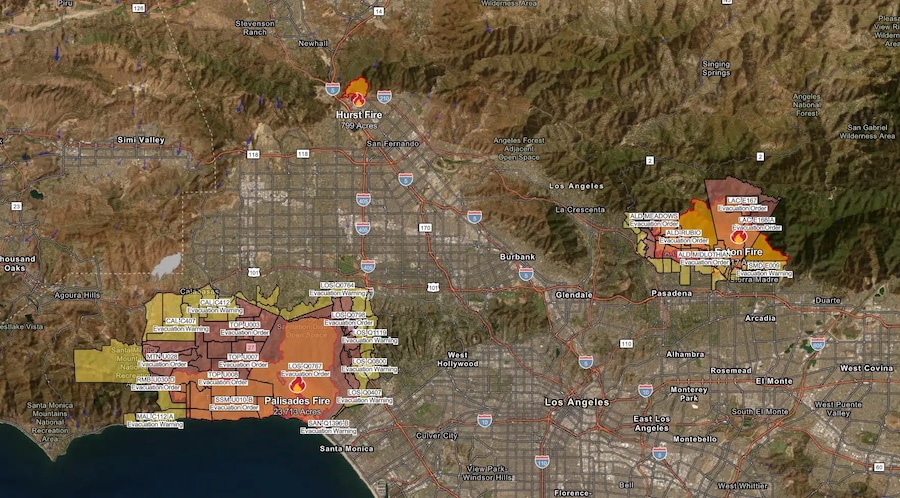
Of the five major fires burning in the Los Angeles area in early January, three are still active. The Hurst fire has burned 799 acres and is 97% contained at the time of writing. The Eaton fire has burned 14,117 acres of the Altadena and Pasadena areas and is currently 35% contained. The largest of the five fires, the Palisades fire, has burned 23,713 acres and is 17% contained as of 8 a.m. PT on Tuesday, January 14, according to data available from CAL FIRE.
Map of active LA fires on Jan. 14, 2025. California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection
Official estimates of the damage have yet to be released; however, AccuWeather meteorologists have estimated the cost of these wildfires to be between $250 billion and $275 billion, an increase from the company’s initial estimates of $135 billion and $150 billion.
“These fast-moving, wind-driven infernos have created one of the costliest wildfire disasters in modern U.S. history,” AccuWeather chief meteorologist Jonathan Porter said in a statement. “Hurricane-force winds sent flames ripping through neighborhoods filled with multi-million-dollar homes. The devastation left behind is heartbreaking, and the economic toll is staggering.”
The Palisades fire burned through a high cost of living area, where homes have a median value of more than $2 million, according to Porter.
“Should a large number of additional structures be burned in the coming days, it may become the worst wildfire in modern California history based on the number of structures burned and economic loss,” Porter added.
However, the economic damage does not just include the cost of multimillion dollar homes, but also lost businesses, relocation costs, job losses and emergency and long-term healthcare costs for fire-related injuries and exposure to poor air quality from the smoke.
“Tragically, lives have been changed forever in just a matter of minutes. Many families may not be able to afford to rebuild or repair and return. Businesses may not be able to recover, and jobs will be permanently lost. Thousands of people are in desperate need of help, initially the basic and life-sustaining needs of food, water and shelter, as this tragedy unfolds,” Porter said. “Many families will face significant unexpected costs to relocate to another area in Southern California. The recovery process will be extremely expensive and emotionally challenging in the months and years to come.”
AccuWeather is not alone in its prediction that this will be the costliest wildfire event in U.S. history. Aon PLC, an insurance broker, and Moody’s, a data analytics company, both echoed the sentiment, although they did not provide cost estimates, The Associated Press reported.
The Los Angeles wildfires are expected to cost at least $20 billion in insured losses, Reuters reported. This would cause these fires to surpass the previous most costly wildfire, the 2018 Camp Fire in Butte County, California, which killed 85 people and cost $12.76 in insured losses.
Residents now fear a worsening housing crisis in the greater Los Angeles area, as rental prices have already started spiking despite a law preventing price increases of more than 10% for housing, food, medical supplies and other essentials during emergencies. As LAist reported, Zillow listings in Los Angeles were found to increase by 15% to 64% in the wake of the fires.
“It will put a squeeze, especially on the adjacent communities,” Michael Lens, a professor of urban planning and public policy at University of California, Los Angeles, told LAist. “That might be particularly acute from the Palisades effect on the Westside.”
The post Los Angeles Fires Lead to Over $200 Billion in Losses, Potentially the Most Expensive Wildfire Event in U.S. History appeared first on EcoWatch.




0 Comments