This post was originally published on Eco Watch
As our planet has experienced increased warming over the last several decades due to greenhouse gas emissions from the burning of fossil fuels, glaciers around the world have been shrinking.
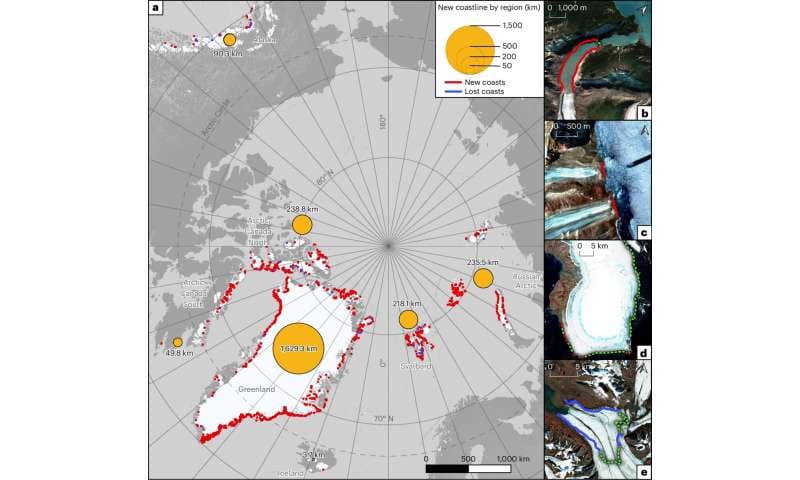
An international team of scientists has found that global heating has, over the past two decades, melted enough of Greenland’s glacial ice that 1,006.6 more miles of coastline have become exposed.
“Accelerated climate warming has caused the majority of marine-terminating glaciers in the Northern Hemisphere to retreat substantially during the twenty-first century,” the authors of the findings wrote in a paper published in Nature Climate Change.
The researchers described how they tracked the receding glaciers by comparing Northern Hemisphere satellite imagery from 2000 to 2020. They used the images to track the exposure of Greenland’s coastline as ice flows heading toward the sea became smaller, reported Phys.org.
“We identified a total of 2,466 ± 0.8 km (123 km a−1) of new coastline with most (66%) of the total length occurring in Greenland,” the scientists wrote in the findings.
The research team was also able to measure individual glaciers along Greenland’s exposed coast. One example was the melting of Zachariae Isstrom, which led to approximately 50 miles of coastline being exposed — two times the amount of any other Northern Hemisphere glacier.
The melting glaciers revealed 35 islands that had been obscured by ice until recently, 29 of which are part of Greenland.
“As marine-terminating glaciers retreat they reveal new coasts that often consist of unconsolidated glacial landforms, such as moraines, eskers, crevasse squeeze ridges or glaciofluvial deposits and deltas, as well as glacially polished bedrock. In some cases, the newly exposed coastline is in the form of rocky islands,” the scientists wrote. “The paraglacial coast exposed from beneath glacial ice differs from much of the Arctic coast as it is not initially affected by permafrost, which needs 2 years or more to aggrade after deglaciation. This lack of permafrost and associated ice cementation means that sediment can be easily eroded, transported and deposited, creating an Arctic system that is geomorphologically uniquely dynamic.”
Spatial distribution and examples of new and lost coastlines in the Arctic from 2000 to 2020. Nature Climate Change (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s41558-025-02282-5
The scientists noted that 13 of the newly exposed islands have not yet been recorded on a map, meaning they have not been claimed by any nation. The discovery could lead to “jockeying” by countries set on accessing potential natural resources the islands could contain.
The retreat of the glaciers poses a risk to local communities in the coastal zone. Regions surrounding marine-terminating glaciers are more susceptible to tsunamis triggered by landslides, the researchers said.
“These young paraglacial coastlines are highly dynamic, exhibiting high sediment fluxes and rapidly evolving landforms. Retreating glaciers and associated newly exposed coastline can have important impacts on local ecosystems and Arctic communities,” the scientists wrote. “Calving fronts of tidewater glaciers, where small tsunamis frequently form are often visited by tourists for their beauty and abundant wildlife.”
The post Climate Change Has Exposed Over 1,000 More Miles of Greenland’s Coastline in 20 Years: Study appeared first on EcoWatch.



0 Comments