This post was originally published on Eco Watch
Alaska is known for its natural beauty and stunning landscapes teeming with vast wilderness and abundant wildlife.
But staining the landscape is a strange phenomenon: Dozens of the most remote rivers and streams in the Land of the Midnight Sun are turning from clear blue to cloudy orange. New research has found that the discoloration could be from the exposure of minerals from thawing permafrost.
“The more we flew around, we started noticing more and more orange rivers and streams,” said Jon O’Donnell, lead author of the study and an ecologist with the National Park Service (NPS)’s Arctic Inventory and Monitoring Network, in a press release from University of California, Davis (UC Davis). “There are certain sites that look almost like a milky orange juice. Those orange streams can be problematic both in terms of being toxic but might also prevent migration of fish to spawning areas.”
For the first time, researchers have sampled and documented some of these degraded waterways, including 75 locations across part of the Brooks Range in northern Alaska.
The researchers said that, as the climate continues to be affected by global heating, these contaminated rivers and streams could seriously impact fisheries and drinking water in Arctic watersheds.
“When the permafrost thaw, sulfide mineral deposits are exposed to groundwater and chemical weathering processes. Through this process, acid, iron and trace metals are released to streams and rivers. Many of these trace metals (such as copper, cadmium, arsenic, and others) are considered toxic for drinking water or for aquatic life if they exceed certain thresholds. We are actively working to determine which metals may exceed thresholds for aquatic life determine[d] by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency,” O’Donnell told EcoWatch in an email.
O’Donnell first became aware of the problem in 2018 while visiting a river that looked rusty but had been clear a year earlier. O’Donnell compiled a list of locations and took water samples when possible. The region is so remote that the rivers and streams are usually only accessible by helicopter.
“The stained rivers are so big we can see them from space,” said Brett Poulin, one of the study’s primary investigators and a UC Davis assistant environmental toxicology professor, in the press release. “These have to be stained a lot to pick them up from space.”
Poulin is a water chemistry expert and thought the staining appeared similar to when water becomes contaminated by acid mine drainage, but there aren’t any mines near any of the degraded rivers.
“Rusting rivers tend to be more acidic and more turbid (due to iron particles). Evidence from the lower 48 has shown that migratory fish like salmon may not pass through river reaches affected by acid mine drainage. Our observations from the Arctic are similar to acid mine drainage, except there are no mines in the affected watersheds. The rivers are draining remote wilderness areas,” O’Donnell told EcoWatch.
One theory is that, as Earth’s climate has warmed, the thawing of frozen permafrost has exposed its minerals to water and oxygen, releasing acid and metals.
“Chemistry tells us minerals are weathering,” Poulin said in the press release. “Understanding what’s in the water is a fingerprint as to what occurred.”
The affected rivers are located on federal lands — including Kobuk Valley and Gates of the Arctic National Parks — managed by the Fish and Wildlife Service, Bureau of Land Management and NPS.
“The Arctic is warming four times faster than the Earth as a whole. Model projections predict continued warming in the coming decades. As the climate warms, permafrost will continue to thaw, exposing previously frozen soils and rocks to chemical weathering. We are working to determine which watersheds in the Brooks Range will be vulnerable to rusting in the future. Not all rivers will turn orange. There needs to be sulfide minerals, such as pyrite, to drive the mobilization of trace metals, sulfate, iron, and acid into the streams,” O’Donnell told EcoWatch.
The river and stream-staining minerals can affect the health of fish and, in turn, the humans who consume them.
“Rusting rivers represent a loss of habitat for fish. Our observations showed a complete loss of resident fish from a stream that changed from clear to orange. Further, metals might accumulate in stream invertebrates, which fish eat, and further accumulate in fish. Thus, eating affected fish has implications for human health. We have not shown this yet, it’s just a concern,” O’Donnell said.
Initial samples were analyzed by Poulin and Taylor Evinger, a Ph.D. candidate in agricultural and environmental chemistry at UC Davis. Other scientists took samples in June and July of 2023, while Poulin and Evinger collected their own in August.
Some samples from the rusted waters had a pH of 2.3 — the average for the rivers is 8. This indicated that the sulfide minerals were weathering, leaving conditions that were highly acidic and corrosive and releasing additional metals. The team measured high or elevated levels of zinc, iron, nickel, cadmium and copper.
“We see a lot of different types of metals in these waters,” Evinger said in the press release. “One of the most dominant metals is iron. That’s what is causing the color change.”
O’Donnell first noted a change in 2018, but satellite images showed stained waters back in 2008.
“The issue is slowly propagating from small headwaters into bigger rivers over time,” Evinger said. “When emergent issues or threats come about, we need to be able to understand them.”
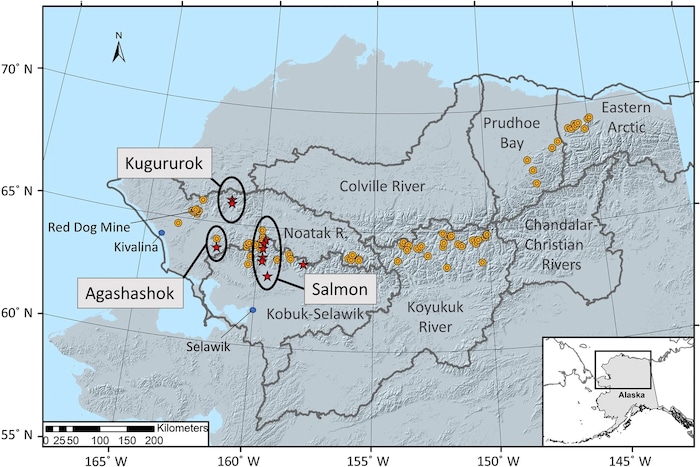
Orange circles indicate orange stream observations, red stars indicate sites where water samples were collected and blue circles are nearby villages. Hydrologic Unit Code-6 basins are shown as black outlines from the National Watershed Boundary dataset. The hill-shade layer utilizes the USGS National Elevation Dataset. Map generated in Esri ArcMap software. Map credit: Kenneth Hill, NPS
The problem of Alaska’s rusting rivers is increasing. Healthy areas are turning into degraded habitats with less fish and invertebrates. Rural communities that rely on the rivers for their drinking water may need to use treatment methods eventually, while fishing stocks could also be affected.
“As the climate continues to warm, we would expect permafrost to continue to thaw and so wherever there are these types of minerals, there’s potential for streams to be turning orange and becoming degraded in terms of water quality,” O’Donnell said in the press release.
However, many of these unsettlingly colorful rivers and streams are far from where people will encounter them.
“While permafrost can be directly impacted by human activity (e.g., roads, buildings, and other infrastructure), much of the permafrost in the Arctic is in remote spots away from towns and cities. Permafrost thaw is due to warming air temperatures which is largely a global issue. As scientists we need to work towards a solution to this problem,” O’Donnell told EcoWatch.
More investigation will be necessary to better comprehend the issues and whether rivers and streams will be able to rebound, possibly after the recovery of permafrost during cold weather.
“We are still working to understand how these rusting rivers change over time, both seasonally and year to year. For instance, streams become less orange during snowmelt, when flows are high and groundwater becomes diluted. Once we understand the mechanisms driving rusting rivers better, we’ll be better able to understand future change and trajectories,” O’Donnell told EcoWatch.
The post Alaska’s Pristine Rivers and Streams Are Turning Orange From Thawing Permafrost, Study Finds appeared first on EcoWatch.




0 Comments